Remote launch
This document discusses the remote launch capabilities of wiredflow. Remote launch is an instruction to execute a program on a remote server. For example, with this mechanism it is possible to run 7 tasks on one virtual machine with 4 GB RAM (A), and 1 task on a machine with 64 GB RAM (B). This is very convenient when one of the tasks requires a lot of resources and executed infrequently.
Problem localization
The first thing to start with is to determine which task is too slow. For example, if the service consists of three pipelines, then first you should determine which pipeline are not effective enough (is it first or second?). Then it is worth defining the stage, which is the "bottleneck". Once you have decided about the stage - it's time to configure remote launch for it.
In the example presented below the core logic may be defined as "bottleneck". Using remote launch the executions time was reduced from 60 seconds to 15:
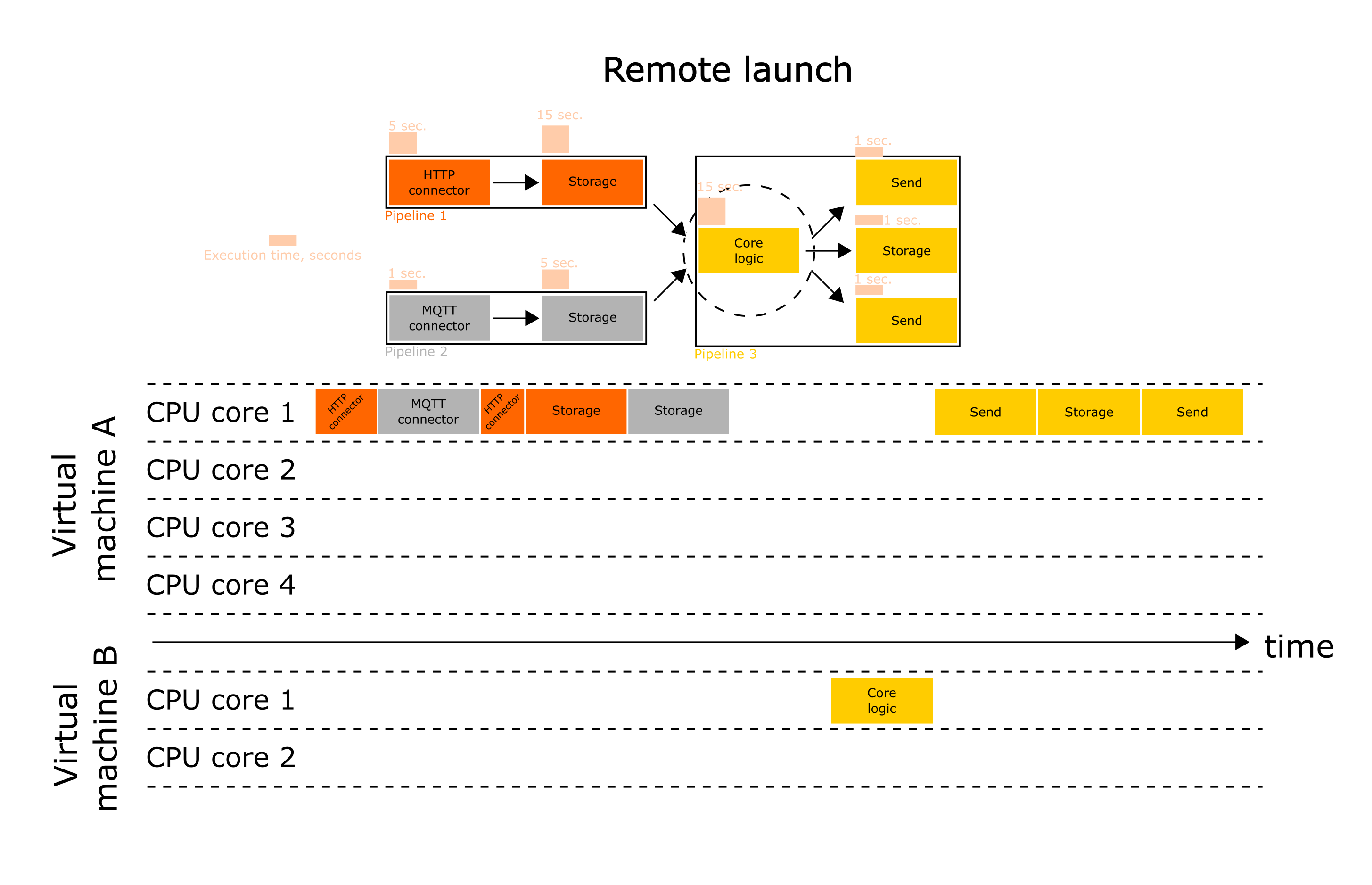
It is worth noting that remote start can be used to launch individual stages - not pipelines and not services.
Custom remote launcher implementation
You can use specialized Python libraries to run tasks remotely (e.g. using SSH to connect to virtual machine), for example:
Then only the custom implementation of the core logic will require modification. The outer service contour (Flow, Pipelines, Stages) will remain unchanged.
Wiredflow as orchestration tool
It is worth have a talk about the role of wiredflow in such hybrid services. In the case where some tasks are run remotely, wiredflow will serve as a single entry point.
During the development of the library, we focused on how the pipelines interact with each other within a single service. This means that wiredflow ensures that if it is computed, it computes every pipeline in its structure. So if something goes wrong in a complex branched system of many servers and pipelines, wiredflow will notice it.
However, this only works if the service is started via a single entry point. If you have configured several wiredflow flows externally (using for example, Kubernetes), then the orchestration must be done externally as well.